02 808 903 67
0474 770 882
info@equitywaterproofing.com.au


Analyzing architectural drawings and section details for design reliability
Evaluating products to ensure they meet requirements and align
with standards


We provide all necessary practice reports such as design compliance review, Material Compliance Review, Performance Solutions, etc…
Ultrasonic thickness testing measures material thickness in waterproofing using waves.

Electronic leak detection testing is a non-destructive technique in waterproofing that uses specialized equipment to locate leaks or moisture in building materials.

Adhesion testing in waterproofing evaluates the bond strength between waterproofing materials and substrates.
Moisture testing in waterproofing assesses water content in materials to ensure effective waterproofing and identify issues.
Thermal photography reveals hidden leaks, inadequate insulation, and compromised areas in building components.
Ultrasonic thickness testing is a non-destructive testing method used in waterproofing to measure the thickness of various materials, such as coatings, membranes, and substrates. It involves the use of ultrasonic waves that are transmitted into the material being tested.
During the test, an ultrasonic transducer is placed on the surface of the material, and a high-frequency sound wave is generated. This sound wave travels through the material and reflects back when it encounters a boundary or change in the material’s density. The time taken for the sound wave to travel to the boundary and back is measured, and this data is used to calculate the thickness of the material.
Ultrasonic thickness testing is particularly useful in waterproofing applications because it can provide accurate measurements without damaging the material or requiring extensive excavation. It allows for quick and efficient evaluation of the thickness of waterproofing layers, ensuring that they meet the specified requirements and are sufficient to prevent water penetration.
This testing method helps in assessing the overall condition of waterproofing systems, identifying any areas where the thickness may be inadequate or where deterioration has occurred. By detecting thickness variations, it enables waterproofing professionals to determine if repairs or additional layers are necessary to maintain the integrity of the waterproofing system.
Overall, ultrasonic thickness testing plays a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of waterproofing systems by providing valuable information about the thickness of materials and facilitating proactive maintenance and repair actions.
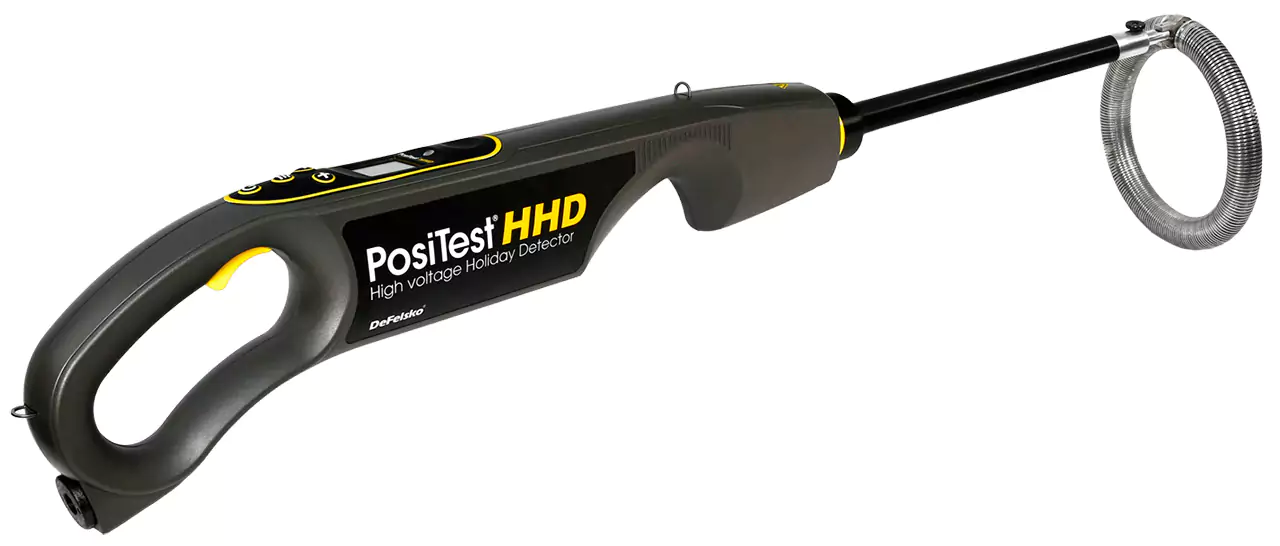

Electronic leak detection testing is a specialized method used in waterproofing to locate and identify leaks or breaches in waterproofing systems. It is a non-destructive testing technique that utilizes electronic equipment to detect the presence of water or moisture within or beneath various building materials.
The process of electronic leak detection testing typically involves the following steps:
Preparation: The area to be tested is prepared by ensuring it is clean, dry, and free from any standing water. The waterproofing system may need to be temporarily exposed or opened to access specific areas for testing.
Test Equipment: Specialized electronic leak detection equipment is used, which typically consists of a low-voltage power supply, conductive testing cables or sensors, and a control unit. The cables or sensors are placed on or in close proximity to the surface being tested.
Testing Method: The equipment applies a low-voltage electrical current to the surface or materials being tested. If there is a breach in the waterproofing system or moisture is present, the electrical current can create a path of least resistance, causing a change in electrical conductivity.
Detection and Localization: The control unit of the electronic leak detection equipment monitors the electrical conductivity and provides real-time feedback. Any changes in electrical conductivity or the presence of moisture are detected and visually or audibly indicated. This helps pinpoint the location of the leak or moisture intrusion.
Reporting: Once the testing is complete, a detailed report is generated, documenting the findings, locations of leaks, and recommendations for necessary repairs or remedial actions.
Electronic leak detection testing is particularly effective in locating leaks or breaches in flat roofs, plaza decks, balconies, and other waterproofing systems where traditional visual inspection may not be sufficient. It can detect leaks even in concealed areas and provide early detection, helping prevent further damage and costly repairs.
By identifying leaks accurately and precisely, electronic leak detection testing helps waterproofing professionals take targeted corrective measures, ensuring the integrity and performance of the waterproofing system. It provides an efficient and reliable method to assess the condition of waterproofing installations and verify their effectiveness in preventing water intrusion.
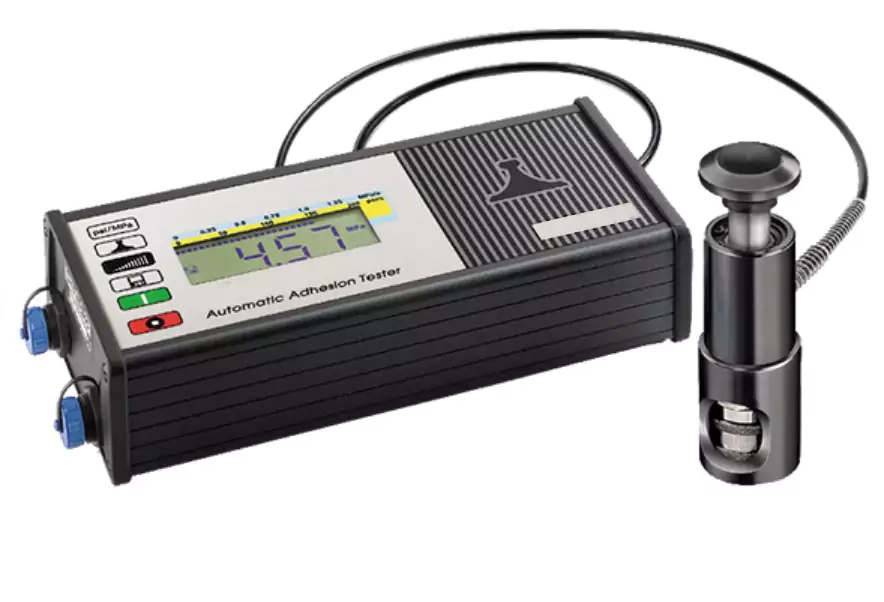

Adhesion testing in waterproofing refers to the evaluation of the bond strength between the waterproofing material or coating and the substrate to which it is applied. It assesses the ability of the waterproofing system to adhere securely to the surface it is intended to protect.
Adhesion is a critical factor in waterproofing because a strong bond ensures that the waterproofing layer remains intact and prevents water from penetrating through gaps or detachment. Adhesion testing helps determine the effectiveness and durability of the waterproofing system by assessing its ability to withstand stress, movement, and environmental conditions.
There are various methods used for adhesion testing in waterproofing, including:
Pull-off test: This method involves attaching a specialized instrument, such as a hydraulic or mechanical pull-off tester, to the waterproofing material. A controlled force is applied to the instrument, exerting a tensile load to pull the material away from the substrate. The maximum force required to detach the material is measured, indicating its adhesion strength.
Tape test: In this test, a pressure-sensitive adhesive tape is firmly applied to the surface of the waterproofing material. After a specified period, the tape is quickly removed, and the appearance and extent of any material transfer or detachment are observed and evaluated.
Cross-cut test: This test involves making a series of perpendicular cuts or incisions through the waterproofing material to create a grid pattern. A piece of adhesive tape is then firmly applied over the cuts and quickly removed. The presence or absence of any material removal along the incisions is examined to assess the adhesion strength.
Wet adhesion test: This test evaluates the adhesion strength of a waterproofing material when subjected to wet conditions. It involves immersing or exposing the material to water or a wetting agent and then performing a pull-off or tape test to assess its adhesion performance under wet conditions.
Adhesion testing helps ensure that the waterproofing system adheres effectively to the substrate, minimizing the risk of water infiltration, premature failures, or delamination. By assessing the bond strength, adhesion testing assists in selecting appropriate waterproofing materials, evaluating installation quality, and identifying areas that may require repairs or improvements.
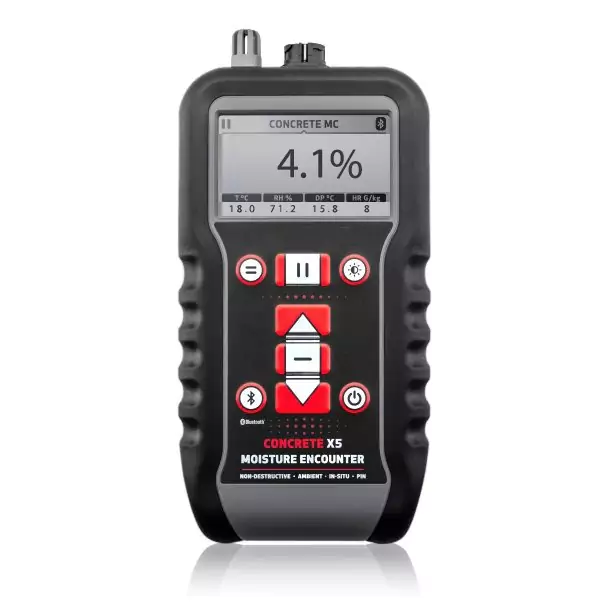

Moisture testing in waterproofing involves assessing the moisture content and presence of water within building materials or structures to evaluate the effectiveness of the waterproofing system and identify potential areas of concern. It is a crucial step in ensuring the integrity and performance of waterproofing installations.
There are several methods used for moisture testing in waterproofing:
Moisture Meters: Moisture meters are handheld devices that measure the moisture content of various materials, such as concrete, wood, or insulation. They work by utilizing electrical conductivity or capacitance to determine the moisture levels within the material. Moisture meters provide immediate readings and are commonly used during inspections or before applying waterproofing materials.
Relative Humidity (RH) Testing: RH testing measures the moisture level within the concrete slab or substrate. It involves placing a specialized RH sensor or probe into a drilled hole within the concrete and allowing it to equilibrate. The sensor measures the relative humidity within the concrete, providing information about the moisture condition and suitability for waterproofing.
Calcium Chloride Testing: Calcium chloride tests are used to assess the moisture vapor emission rate (MVER) from concrete slabs. It involves placing a small dish containing calcium chloride on the concrete surface and covering it with a sealed dome. Over a specific period, the dish absorbs moisture from the concrete, and its weight gain is measured. The weight gain indicates the amount of moisture being emitted by the concrete.
Infrared Thermography: Infrared thermography utilizes thermal imaging cameras to detect temperature differences on the surface of materials. Moisture within building materials often results in temperature variations, which can be identified through thermal imaging. This method helps identify potential areas of water intrusion or moisture accumulation behind walls, roofs, or other surfaces.
Moisture testing in waterproofing plays a vital role in preventing water damage, mold growth, and structural deterioration. By assessing the moisture content and presence of water, it helps determine the need for appropriate waterproofing measures, such as membranes, coatings, or sealants. It also assists in diagnosing existing moisture-related issues, guiding repairs and remediation efforts to ensure a dry and protected building envelope.
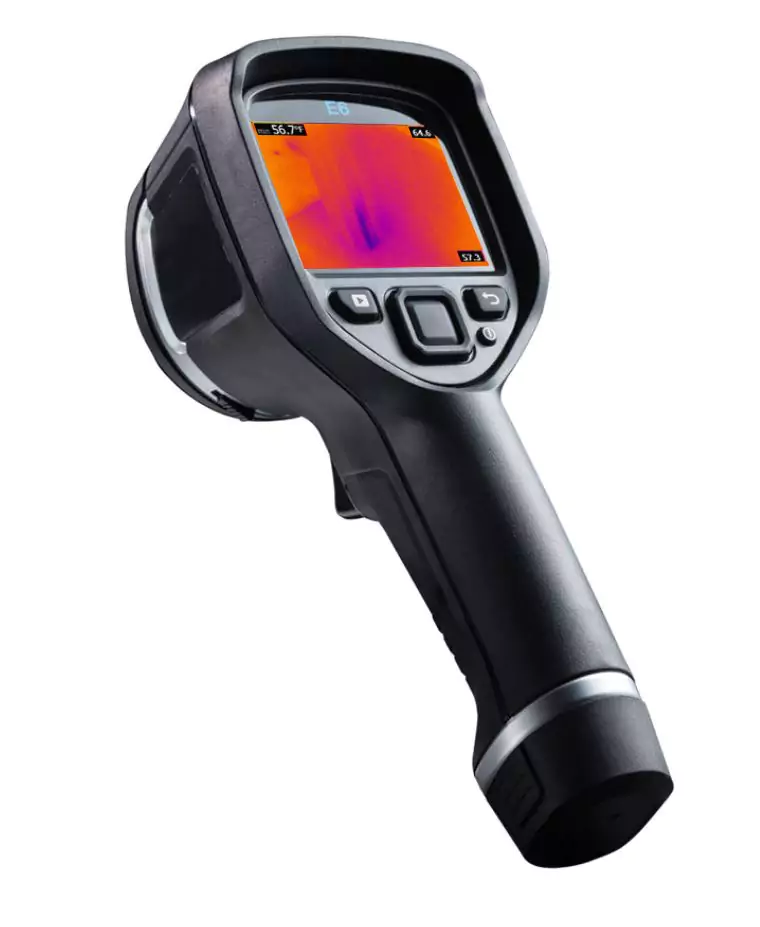

Thermal photography testing” is not a standard term in waterproofing. However, thermal imaging or infrared thermography is a commonly used method in the construction industry, including waterproofing, for identifying thermal anomalies or temperature differences on the surface of materials or structures.
Thermal imaging cameras detect and measure the infrared radiation emitted by objects or surfaces, allowing the visualization of temperature variations. In the context of waterproofing, thermal imaging is used to identify areas of potential water intrusion, moisture accumulation, or insulation deficiencies. By detecting temperature differences, it can indicate the presence of hidden leaks, moisture penetration, or inadequate insulation in walls, roofs, or other building components.
When conducting thermal imaging for waterproofing purposes, an infrared camera is used to capture images or videos that represent the temperature distribution on the surface being inspected. Warmer or cooler areas than the surrounding environment can indicate the presence of moisture, water leaks, or areas where the insulation is compromised.
Thermal imaging can be particularly useful in identifying water leaks within walls, roofs, or building envelopes, as it can detect temperature variations caused by evaporative cooling. It can also help locate areas of poor insulation or thermal bridging, which can contribute to moisture-related issues or energy inefficiency.
By utilizing thermal imaging in waterproofing, professionals can identify and address potential problems before they become more significant issues. It allows for early detection of water intrusion, helps target repairs or maintenance efforts, and ensures the integrity and performance of the waterproofing system.
It’s important to note that while thermal imaging can provide valuable insights, it is typically used as a screening tool and should be complemented by other diagnostic methods to confirm the presence of water or moisture-related problems and determine their exact cause.
02 808 903 67
0474 770 882
info@equitywaterproofing.com.au

Thermal photography testing” is not a standard term in waterproofing. However, thermal imaging or infrared thermography is a commonly used method in the construction industry, including waterproofing, for identifying thermal anomalies or temperature differences on the surface of materials or structures.
Thermal imaging cameras detect and measure the infrared radiation emitted by objects or surfaces, allowing the visualization of temperature variations. In the context of waterproofing, thermal imaging is used to identify areas of potential water intrusion, moisture accumulation, or insulation deficiencies. By detecting temperature differences, it can indicate the presence of hidden leaks, moisture penetration, or inadequate insulation in walls, roofs, or other building components.
When conducting thermal imaging for waterproofing purposes, an infrared camera is used to capture images or videos that represent the temperature distribution on the surface being inspected. Warmer or cooler areas than the surrounding environment can indicate the presence of moisture, water leaks, or areas where the insulation is compromised.
Thermal imaging can be particularly useful in identifying water leaks within walls, roofs, or building envelopes, as it can detect temperature variations caused by evaporative cooling. It can also help locate areas of poor insulation or thermal bridging, which can contribute to moisture-related issues or energy inefficiency.
By utilizing thermal imaging in waterproofing, professionals can identify and address potential problems before they become more significant issues. It allows for early detection of water intrusion, helps target repairs or maintenance efforts, and ensures the integrity and performance of the waterproofing system.
It’s important to note that while thermal imaging can provide valuable insights, it is typically used as a screening tool and should be complemented by other diagnostic methods to confirm the presence of water or moisture-related problems and determine their exact cause.

Moisture testing in waterproofing involves assessing the moisture content and presence of water within building materials or structures to evaluate the effectiveness of the waterproofing system and identify potential areas of concern. It is a crucial step in ensuring the integrity and performance of waterproofing installations.
There are several methods used for moisture testing in waterproofing:
Moisture Meters: Moisture meters are handheld devices that measure the moisture content of various materials, such as concrete, wood, or insulation. They work by utilizing electrical conductivity or capacitance to determine the moisture levels within the material. Moisture meters provide immediate readings and are commonly used during inspections or before applying waterproofing materials.
Relative Humidity (RH) Testing: RH testing measures the moisture level within the concrete slab or substrate. It involves placing a specialized RH sensor or probe into a drilled hole within the concrete and allowing it to equilibrate. The sensor measures the relative humidity within the concrete, providing information about the moisture condition and suitability for waterproofing.
Calcium Chloride Testing: Calcium chloride tests are used to assess the moisture vapor emission rate (MVER) from concrete slabs. It involves placing a small dish containing calcium chloride on the concrete surface and covering it with a sealed dome. Over a specific period, the dish absorbs moisture from the concrete, and its weight gain is measured. The weight gain indicates the amount of moisture being emitted by the concrete.
Infrared Thermography: Infrared thermography utilizes thermal imaging cameras to detect temperature differences on the surface of materials. Moisture within building materials often results in temperature variations, which can be identified through thermal imaging. This method helps identify potential areas of water intrusion or moisture accumulation behind walls, roofs, or other surfaces.
Moisture testing in waterproofing plays a vital role in preventing water damage, mold growth, and structural deterioration. By assessing the moisture content and presence of water, it helps determine the need for appropriate waterproofing measures, such as membranes, coatings, or sealants. It also assists in diagnosing existing moisture-related issues, guiding repairs and remediation efforts to ensure a dry and protected building envelope.

Adhesion testing in waterproofing refers to the evaluation of the bond strength between the waterproofing material or coating and the substrate to which it is applied. It assesses the ability of the waterproofing system to adhere securely to the surface it is intended to protect.
Adhesion is a critical factor in waterproofing because a strong bond ensures that the waterproofing layer remains intact and prevents water from penetrating through gaps or detachment. Adhesion testing helps determine the effectiveness and durability of the waterproofing system by assessing its ability to withstand stress, movement, and environmental conditions.
There are various methods used for adhesion testing in waterproofing, including:
Pull-off test: This method involves attaching a specialized instrument, such as a hydraulic or mechanical pull-off tester, to the waterproofing material. A controlled force is applied to the instrument, exerting a tensile load to pull the material away from the substrate. The maximum force required to detach the material is measured, indicating its adhesion strength.
Tape test: In this test, a pressure-sensitive adhesive tape is firmly applied to the surface of the waterproofing material. After a specified period, the tape is quickly removed, and the appearance and extent of any material transfer or detachment are observed and evaluated.
Cross-cut test: This test involves making a series of perpendicular cuts or incisions through the waterproofing material to create a grid pattern. A piece of adhesive tape is then firmly applied over the cuts and quickly removed. The presence or absence of any material removal along the incisions is examined to assess the adhesion strength.
Wet adhesion test: This test evaluates the adhesion strength of a waterproofing material when subjected to wet conditions. It involves immersing or exposing the material to water or a wetting agent and then performing a pull-off or tape test to assess its adhesion performance under wet conditions.
Adhesion testing helps ensure that the waterproofing system adheres effectively to the substrate, minimizing the risk of water infiltration, premature failures, or delamination. By assessing the bond strength, adhesion testing assists in selecting appropriate waterproofing materials, evaluating installation quality, and identifying areas that may require repairs or improvements.

Electronic leak detection testing is a specialized method used in waterproofing to locate and identify leaks or breaches in waterproofing systems. It is a non-destructive testing technique that utilizes electronic equipment to detect the presence of water or moisture within or beneath various building materials.
The process of electronic leak detection testing typically involves the following steps:
Preparation: The area to be tested is prepared by ensuring it is clean, dry, and free from any standing water. The waterproofing system may need to be temporarily exposed or opened to access specific areas for testing.
Test Equipment: Specialized electronic leak detection equipment is used, which typically consists of a low-voltage power supply, conductive testing cables or sensors, and a control unit. The cables or sensors are placed on or in close proximity to the surface being tested.
Testing Method: The equipment applies a low-voltage electrical current to the surface or materials being tested. If there is a breach in the waterproofing system or moisture is present, the electrical current can create a path of least resistance, causing a change in electrical conductivity.
Detection and Localization: The control unit of the electronic leak detection equipment monitors the electrical conductivity and provides real-time feedback. Any changes in electrical conductivity or the presence of moisture are detected and visually or audibly indicated. This helps pinpoint the location of the leak or moisture intrusion.
Reporting: Once the testing is complete, a detailed report is generated, documenting the findings, locations of leaks, and recommendations for necessary repairs or remedial actions.
Electronic leak detection testing is particularly effective in locating leaks or breaches in flat roofs, plaza decks, balconies, and other waterproofing systems where traditional visual inspection may not be sufficient. It can detect leaks even in concealed areas and provide early detection, helping prevent further damage and costly repairs.
By identifying leaks accurately and precisely, electronic leak detection testing helps waterproofing professionals take targeted corrective measures, ensuring the integrity and performance of the waterproofing system. It provides an efficient and reliable method to assess the condition of waterproofing installations and verify their effectiveness in preventing water intrusion.

Ultrasonic thickness testing is a non-destructive testing method used in waterproofing to measure the thickness of various materials, such as coatings, membranes, and substrates. It involves the use of ultrasonic waves that are transmitted into the material being tested.
During the test, an ultrasonic transducer is placed on the surface of the material, and a high-frequency sound wave is generated. This sound wave travels through the material and reflects back when it encounters a boundary or change in the material’s density. The time taken for the sound wave to travel to the boundary and back is measured, and this data is used to calculate the thickness of the material.
Ultrasonic thickness testing is particularly useful in waterproofing applications because it can provide accurate measurements without damaging the material or requiring extensive excavation. It allows for quick and efficient evaluation of the thickness of waterproofing layers, ensuring that they meet the specified requirements and are sufficient to prevent water penetration.
This testing method helps in assessing the overall condition of waterproofing systems, identifying any areas where the thickness may be inadequate or where deterioration has occurred. By detecting thickness variations, it enables waterproofing professionals to determine if repairs or additional layers are necessary to maintain the integrity of the waterproofing system.
Overall, ultrasonic thickness testing plays a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of waterproofing systems by providing valuable information about the thickness of materials and facilitating proactive maintenance and repair actions.